If We Could Just Get Adults to Be More Curious Like Young People

Nine months ago, I met with a fine group of Scouts on a job site to answer their questions about construction and business. If adults would ask more questions like this…there would be less confusion between customer and contractor.
Too often as adults we don’t ask questions for fear that we will appear dumb. It’s like we think we should know everything about everything. As I answered their questions, I thought…
If more people asked questions like these , more dream projects would be a dream come true.
Here’s the questions they asked:
- How much does building a new house cost?
- How much wood does a new house take?
- How long does it take to build a new house?
- How many permits do you need to build a new house?
- Do you build specially for earthquakes?
- What equipment do you use most often?
- How do you dig a foundation?
- Did you go to college? Trade school?
- What schooling do you need?
- What made you want to start your business?
- What was the first thing you built?
- What was your first job ever?
- How much steel goes into a house?
- Have you ever built a tiny house?
- Where are the dangerous places in a construction site?
- Do you do more commercial or residential work?
- Do you prefer/use more manual or electrical equipment?
- Do you do more renovations or new building projects?
- Have you ever broken a hard hat?
- How often do injuries happen?
- Do you hire out the electrical/plumbing or does the owner?

I thought I should share the answers to their questions with you. Due to the length of the list, I will it break down in future posts by category. Maybe these will inspire more questions to be asked. At the very least you will have these answers.
Check back next week to see the answers.
Communication is the biggest problem for construction customers and contractors. That’s why I have written extensively about it in the past. Here are links to some of those posts:
- What should be included in contractor’s communication
- There’s a high cost to no communication
- How to keep your construction project from falling apart
- Building a house can be scary, but it doesn’t have to be
- What we have here is a failure to communication
- Good communication isn’t a one-way street
- The value of a professional builder
- What’s the cost of cheap

If you or someone you know have a construction question, please post it in the comments below and I will answer it too.










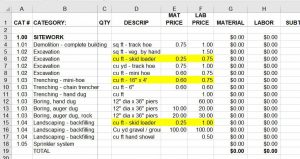
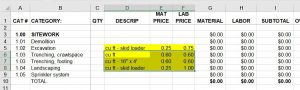

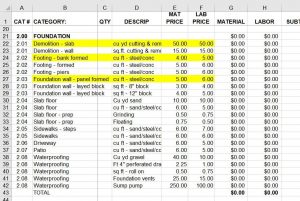
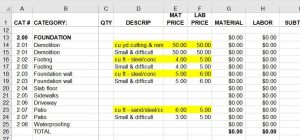






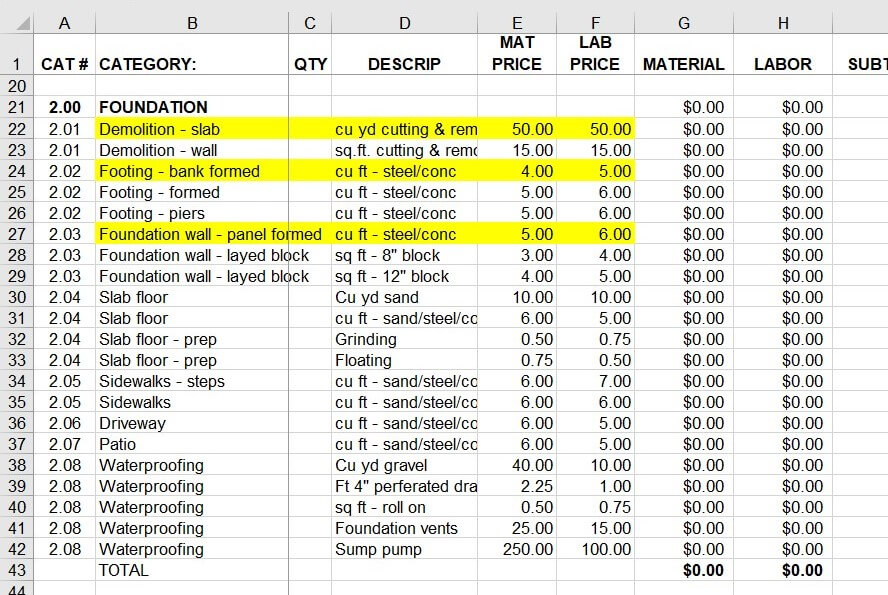
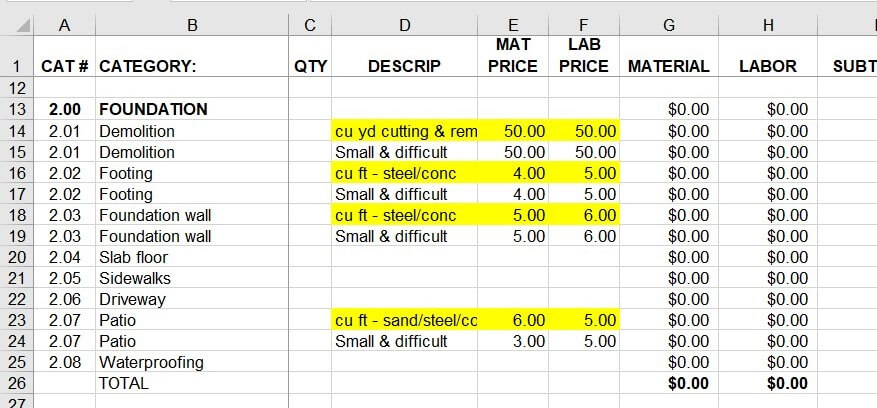

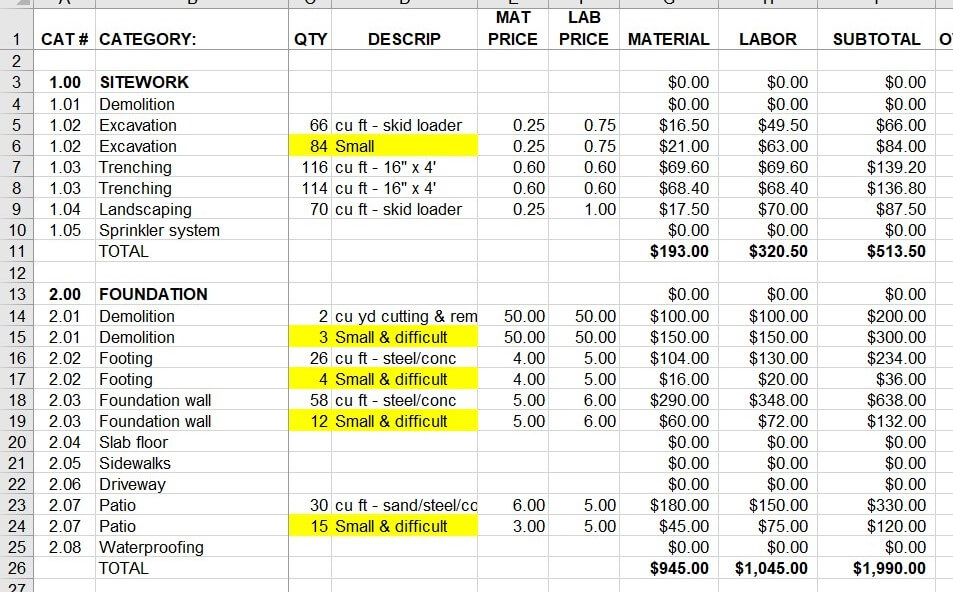












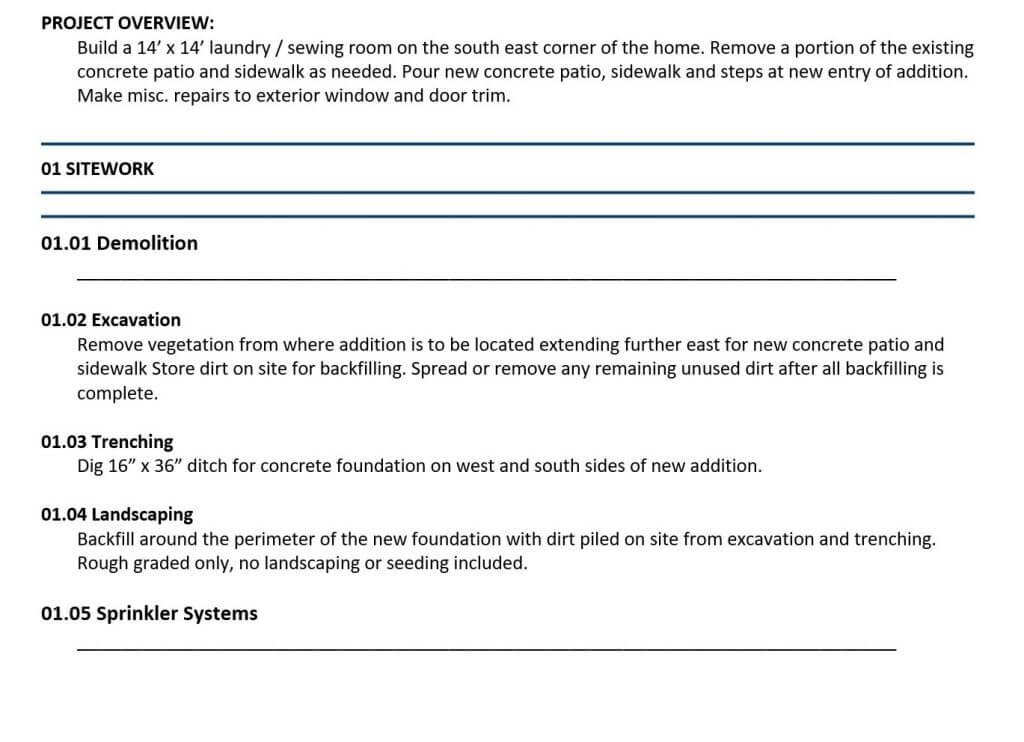







 He asked if this was a problem. My partner told him no, it wasn’t a problem. Guess what…
He asked if this was a problem. My partner told him no, it wasn’t a problem. Guess what…
 What if I told you that there is such a system and you could have it? There is and it’s going to become available in the next few months. Over the next several weeks we are going to breakdown the system, go through the different documents and processes in detail and explain how it works.
What if I told you that there is such a system and you could have it? There is and it’s going to become available in the next few months. Over the next several weeks we are going to breakdown the system, go through the different documents and processes in detail and explain how it works.


 Trying to DO EVERYTHING for EVERYBODY has been something that I have always struggled with. There’s just so many great things to be done and someone needs to do them. It never works any time anybody tries it. We have to learn to say no.
Trying to DO EVERYTHING for EVERYBODY has been something that I have always struggled with. There’s just so many great things to be done and someone needs to do them. It never works any time anybody tries it. We have to learn to say no.



 Quality, honesty and integrity cover this part of the list. These are character issues. They are about choosing to give as much importance to someone else’s needs as I do my own.
Quality, honesty and integrity cover this part of the list. These are character issues. They are about choosing to give as much importance to someone else’s needs as I do my own. The entire issue of construction projects falling apart is unnecessary and unacceptable.
The entire issue of construction projects falling apart is unnecessary and unacceptable.