This Seems to Be Especially Prevalent in The Construction Industry
I was visiting with some people recently about the disappointing number of companies signing up for the upcoming Blueprint for Building a Better Proposal workshop. I’ve seen the results of poor communication between contractor and customer. This workshop would help with this problem.

Every one of the people I was talking with said the same thing. “They’re contractors, they’re not going to sign up until the last minute. I wouldn’t be surprised if they just show up.”
Later I visited with a few different construction company owners and asked if they were coming to the workshop. Their answers were eerily similar…I’m not sure if I have time. I’ve got a lot of work scheduled. I’m not sure that I can afford to take a day off work. I’ll have to wait and see how things are going.”
Why would this be a problem in construction more than other industries?
I don’t know if it is more of an issue in construction than anywhere else or if it just seems that way because that’s where my focus is. There are a few things that I think contribute to this situation, construction or not.
Why are there so many that aren’t signing up for the workshop?

We’re too busy – We’ve said yes to too many things. We feel pulled in so many different directions. It’s common to hear people say, “I don’t have enough time.” Most of us overbook and then spend most of our time fighting the hottest fire. My argument is –
God has given us enough time…it’s up to us to invest it wisely.

We struggle with prioritizing – I’ve got this important project that I’m working on. It’s more important than learning something new. Every day we are learning in a variety of ways. The question is, which is the better investment, learning from “on the job mistakes” or from someone else’s. On the job mistakes can be very costly.
Learning from what someone else has learned is a good investment.

Not sure if that training is for me – How will you ever know if you don’t check it out? Most of the time our uncertainty is fear. We’re afraid to learn new things. “I’ve managed to get along just fine so far”. Wouldn’t it be nice to have a predesigned system that would improve your communication and increase your accuracy? The question is…
How long can “getting along just fine” be sustained?

I can’t afford it – Things are tight right now. Profits are down. Maybe I can do it next time. What if your out of business before the next time. There is a cost to any kind of schooling formal or otherwise. How long can you afford to not invest in yourself?
Investing in this workshop now, improves your odds for a brighter future.

I don’t know if the construction industry procrastinates more than any other. What I do know is, if you’re in the construction industry, time is running out to invest in yourself and your business. Don’t put it off any longer. Stop procrastinating and get signed up for the Blueprint for Building a Better Proposal workshop.
If you or someone you know would benefit from learning how to do better proposals, sign up here.



 I’ve answered 11 of the 21
I’ve answered 11 of the 21  I do more residential than commercial but do both. Commercial tends to be less relational than residential. I’ve always felt like the relationship between the customer and contractor is more than only a business transaction. In order to serve the customer well I need to get to know them. This only happens if a relationship is built. Commercial projects normally are more transactional.
I do more residential than commercial but do both. Commercial tends to be less relational than residential. I’ve always felt like the relationship between the customer and contractor is more than only a business transaction. In order to serve the customer well I need to get to know them. This only happens if a relationship is built. Commercial projects normally are more transactional. I do mostly renovations and remodeling projects. New construction is less challenging than remodeling. New construction has less restraints than renovations do. It takes more out of the box thinking to take an already existing structure and change it into something different. I love the challenge of finding a solution to these projects.
I do mostly renovations and remodeling projects. New construction is less challenging than remodeling. New construction has less restraints than renovations do. It takes more out of the box thinking to take an already existing structure and change it into something different. I love the challenge of finding a solution to these projects. No. In this part of the country this hasn’t even been a part of the discussion up until recently. It still isn’t a big issue for local construction projects. If buildings are built up to the current building codes for our area, past tremors won’t be any reason to change this. Our focus should be on high winds and tornados.
No. In this part of the country this hasn’t even been a part of the discussion up until recently. It still isn’t a big issue for local construction projects. If buildings are built up to the current building codes for our area, past tremors won’t be any reason to change this. Our focus should be on high winds and tornados. This depends on where the building project is located, some places don’t require any. Normally there is at least one “building permit” for each project. There are also different permits for different areas of the project, i.e. plumbing, electrical, HVAC, etc. that are sometimes required. All permitting is determined by the local jurisdiction, so it is important to find out what the regulations are for the location where you plan to build before you start.
This depends on where the building project is located, some places don’t require any. Normally there is at least one “building permit” for each project. There are also different permits for different areas of the project, i.e. plumbing, electrical, HVAC, etc. that are sometimes required. All permitting is determined by the local jurisdiction, so it is important to find out what the regulations are for the location where you plan to build before you start.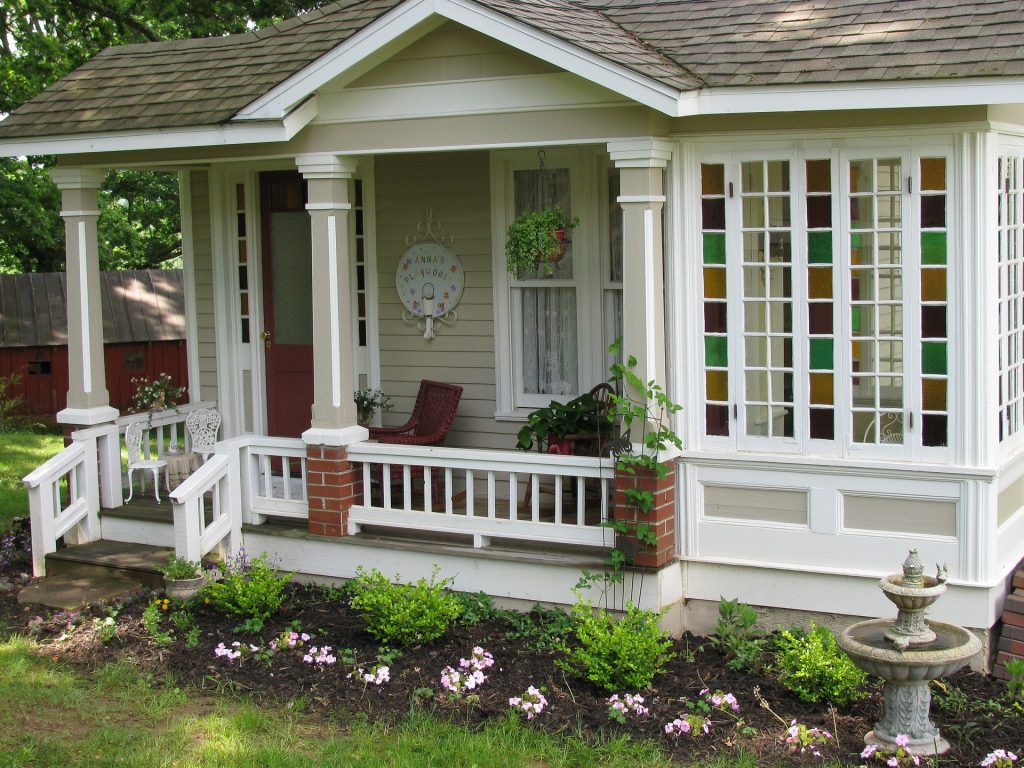 Your definition of a “tiny house” will depend on how I answer this question. I have built three very tiny houses. None of these were built for living in, not that someone couldn’t have. The three tiny houses were built for playhouses but were more than a normal playhouse. All of them were built with the same construction as a full-size house…just smaller…a lot smaller.
Your definition of a “tiny house” will depend on how I answer this question. I have built three very tiny houses. None of these were built for living in, not that someone couldn’t have. The three tiny houses were built for playhouses but were more than a normal playhouse. All of them were built with the same construction as a full-size house…just smaller…a lot smaller.
 This is the 3rd in the series of answering the questions asked by the Scout group. The
This is the 3rd in the series of answering the questions asked by the Scout group. The  This will vary on each project and will depend on the customer’s needs and goals, but as a general contractor I usually provide subcontractors. As an example of varying
This will vary on each project and will depend on the customer’s needs and goals, but as a general contractor I usually provide subcontractors. As an example of varying  between projects, the owner of the project we’re currently working on is a retired electrician, so he’s doing the wiring on this project.
between projects, the owner of the project we’re currently working on is a retired electrician, so he’s doing the wiring on this project. I think the piece of equipment that I use the most often is a hammer. Some people would probably consider equipment as something motorized or powered. According to
I think the piece of equipment that I use the most often is a hammer. Some people would probably consider equipment as something motorized or powered. According to  Here we are again, manual vs. powered. I definitely “prefer” using electrical equipment or most any power tool over manual. Power tools make most tasks they’re used for easier. However, depending on the task being performed in some cases the manual tool is better suited and more productive. For example, you shouldn’t use a pneumatic nail gun as a hammer to drive a board into place.
Here we are again, manual vs. powered. I definitely “prefer” using electrical equipment or most any power tool over manual. Power tools make most tasks they’re used for easier. However, depending on the task being performed in some cases the manual tool is better suited and more productive. For example, you shouldn’t use a pneumatic nail gun as a hammer to drive a board into place. The size of the project will usually dictate how the foundation will be dug. If the project requires moving a large amount of dirt, for example a basement, then typically a large excavator (link) will be used. If it’s something
The size of the project will usually dictate how the foundation will be dug. If the project requires moving a large amount of dirt, for example a basement, then typically a large excavator (link) will be used. If it’s something smaller, we would most often use a mini excavator. (link) If the project is small enough or inaccessible to equipment then it could be dug by hand with a shovel.
smaller, we would most often use a mini excavator. (link) If the project is small enough or inaccessible to equipment then it could be dug by hand with a shovel.
 This answer depends on how we want to define “injury”. Some people would consider a splinter an injury. For this answer I’m going to define injury as something requiring medical attention, i.e. stiches, broken bones, requiring a doctor’s attention, etc. During my forty plus years in construction I have personally witnessed or actually been injured 8 – 10 times. If I take that number of times over the forty years, that’s .000137%. As dangerous as construction sites are and as much construction that’s done, surprisingly it’s not as often as one might expect. The key is working smart and safe.
This answer depends on how we want to define “injury”. Some people would consider a splinter an injury. For this answer I’m going to define injury as something requiring medical attention, i.e. stiches, broken bones, requiring a doctor’s attention, etc. During my forty plus years in construction I have personally witnessed or actually been injured 8 – 10 times. If I take that number of times over the forty years, that’s .000137%. As dangerous as construction sites are and as much construction that’s done, surprisingly it’s not as often as one might expect. The key is working smart and safe. This is one of the most interesting questions asked and easiest to answer. I can answer it with a resounding NO. This is not to say they can’t be broken, but it takes a lot to break one.
This is one of the most interesting questions asked and easiest to answer. I can answer it with a resounding NO. This is not to say they can’t be broken, but it takes a lot to break one.
 As I pointed out last week, due to the number of questions I’m going to divide them into different topics to keep the posts from getting too long. This week I’ll start by answering some basic construction questions. Keep in mind that asking and answering questions is communication and communication is a two-way process. This means that before I can answer questions fully and accurately, I need some questions answered.
As I pointed out last week, due to the number of questions I’m going to divide them into different topics to keep the posts from getting too long. This week I’ll start by answering some basic construction questions. Keep in mind that asking and answering questions is communication and communication is a two-way process. This means that before I can answer questions fully and accurately, I need some questions answered. This is the most common first question. It only makes sense; cost is a critical part of deciding whether to build. It’s also one of the most difficult to answer, especially when asked without any specifics.
This is the most common first question. It only makes sense; cost is a critical part of deciding whether to build. It’s also one of the most difficult to answer, especially when asked without any specifics. The answer to this question will be directly connected to the answers of the last question. Size, design, level of finish, etc. will all effect the length of time to build a new house. An average 2000 square foot home will take 6 – 9 months.
The answer to this question will be directly connected to the answers of the last question. Size, design, level of finish, etc. will all effect the length of time to build a new house. An average 2000 square foot home will take 6 – 9 months. Once again, the answer is going to depend on specifics of the house. Let’s just answer the question using the average 2000 square foot house that we have been using. Let’s assume that it’s going to have wood floor joists, sub-floor, wall studs, wall boxing, ceiling joists, rafters, roof sheathing, siding, windows, doors, cabinets, etc. All these things combined will be around 40 pounds per square foot. That means the wood used in a 2000 square foot house will weigh around 80,000 pounds, or 40 tons.
Once again, the answer is going to depend on specifics of the house. Let’s just answer the question using the average 2000 square foot house that we have been using. Let’s assume that it’s going to have wood floor joists, sub-floor, wall studs, wall boxing, ceiling joists, rafters, roof sheathing, siding, windows, doors, cabinets, etc. All these things combined will be around 40 pounds per square foot. That means the wood used in a 2000 square foot house will weigh around 80,000 pounds, or 40 tons. There are some cases where houses are framed using steel, but typically that’s not very common. There are some steel things commonly used, like nails, screws, joist hangers, reinforcing steel in concrete, etc. Sometimes steel beams and posts are used for supporting heavier loads and wider spans. In a typical wood framed house, it takes around 10 pounds of steel reinforcing, fasteners and misc. per square foot to build. This means that our 2000 square foot wood framed home would have around 20,000 pounds or 10 tons.
There are some cases where houses are framed using steel, but typically that’s not very common. There are some steel things commonly used, like nails, screws, joist hangers, reinforcing steel in concrete, etc. Sometimes steel beams and posts are used for supporting heavier loads and wider spans. In a typical wood framed house, it takes around 10 pounds of steel reinforcing, fasteners and misc. per square foot to build. This means that our 2000 square foot wood framed home would have around 20,000 pounds or 10 tons.














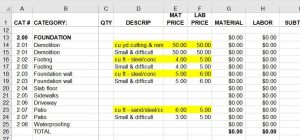

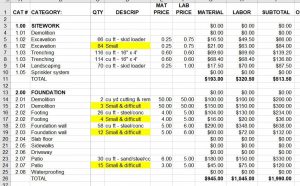





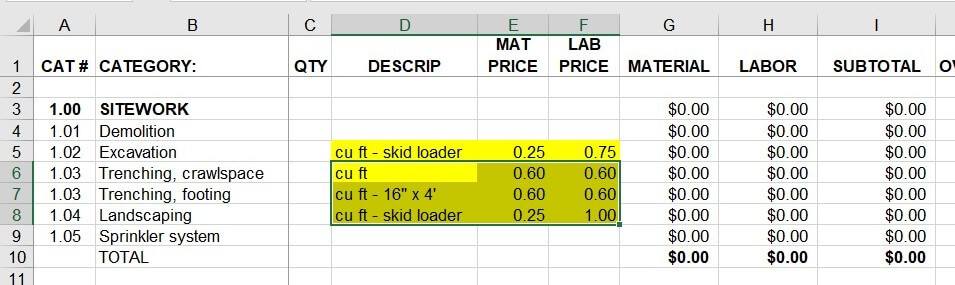
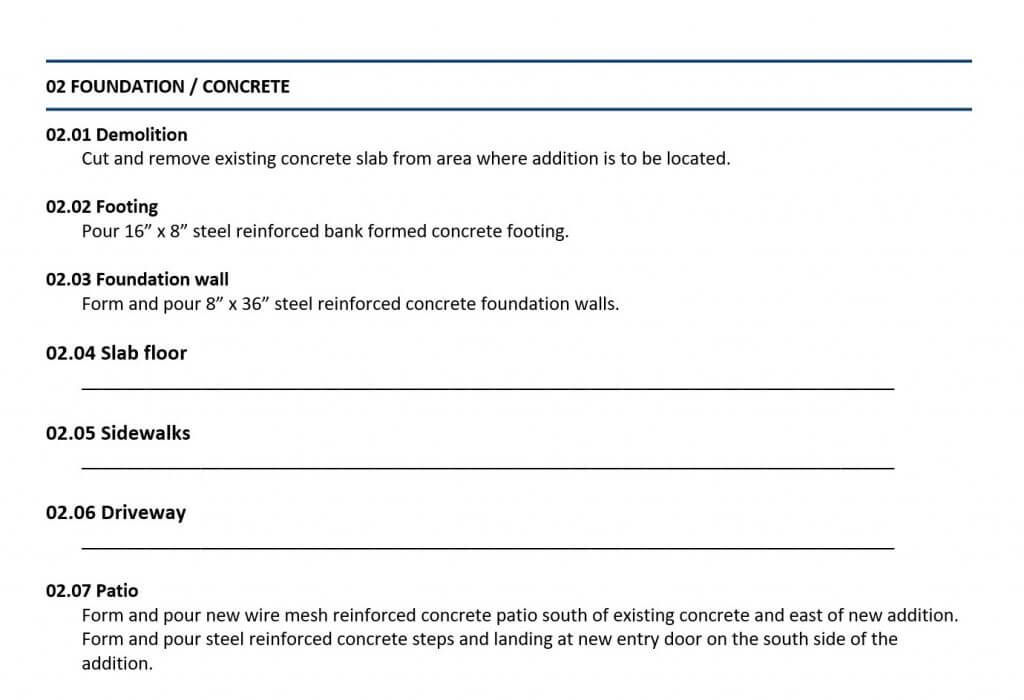
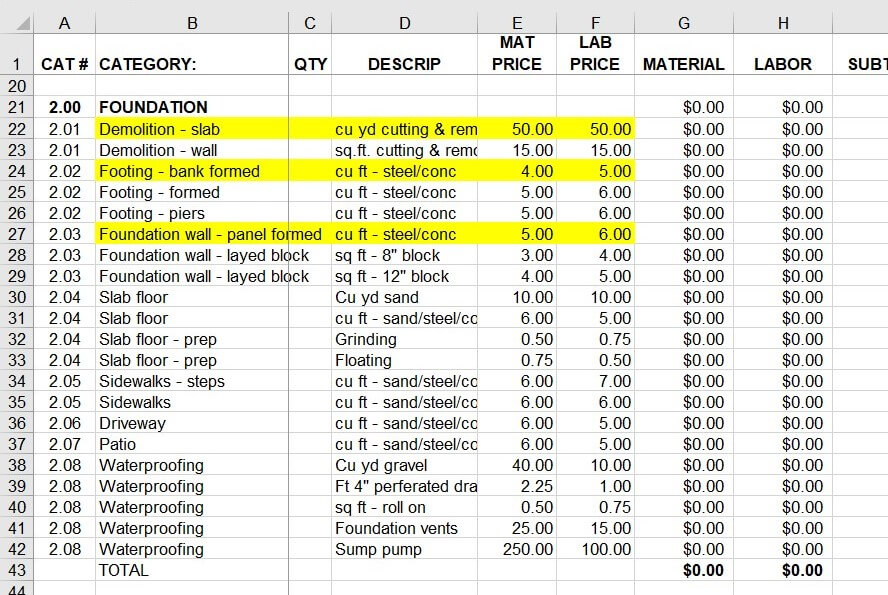
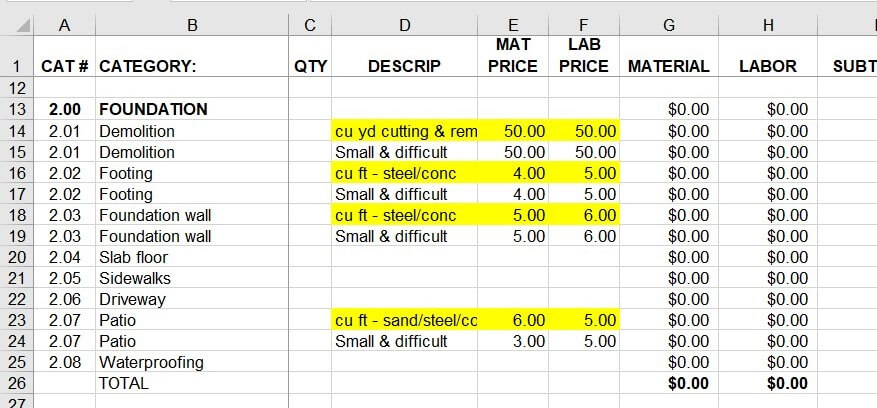

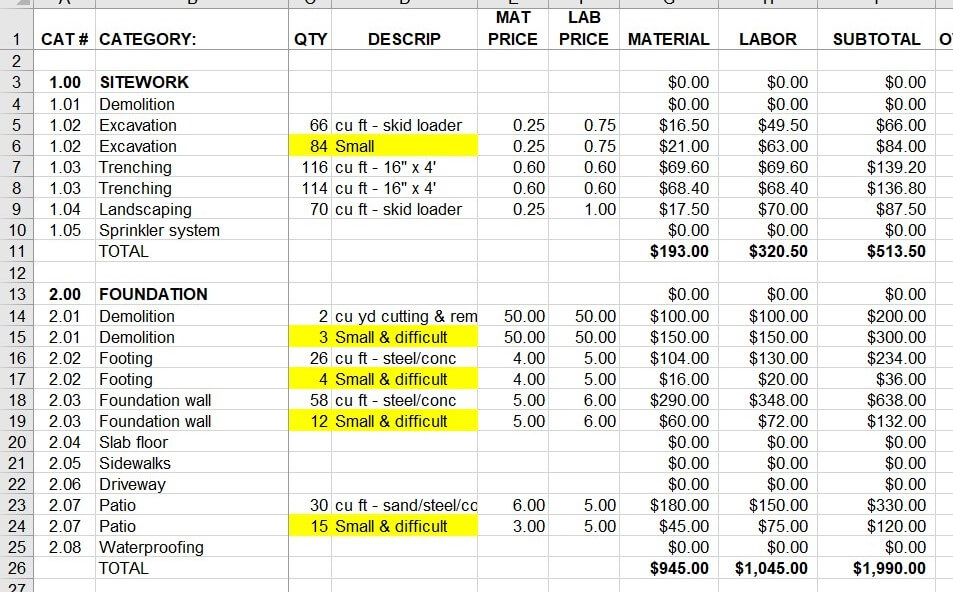



 In the first post of this Blueprint for Building A Better Proposal series, I wrote about this communication problem and that
In the first post of this Blueprint for Building A Better Proposal series, I wrote about this communication problem and that 




 In the first post of this Blueprint for Building A Better Proposal series, I wrote about this communication problem and that
In the first post of this Blueprint for Building A Better Proposal series, I wrote about this communication problem and that 

